Embark on a journey into the enigmatic world of genetics with our comprehensive DNA Double Helix Worksheet Answer Key. Delve into the intricate structure of DNA, the blueprint of life, and uncover the fundamental principles that govern its replication, transcription, and translation.
This in-depth resource empowers students and educators alike to grasp the complexities of molecular biology with clarity and precision.
Unveiling the significance of the DNA double helix discovery, we embark on an exploration of its unique architecture, base pairing, and the remarkable stability it imparts to the DNA molecule. Witness the intricate dance of DNA replication, deciphering the role of enzymes and the critical importance of this process for cell division and growth.
Our odyssey continues into the realm of DNA transcription, where we illuminate the function of RNA polymerase and its pivotal role in protein synthesis.
DNA Structure
The discovery of the DNA double helix in 1953 by James Watson and Francis Crick was a pivotal moment in the history of biology. This breakthrough laid the foundation for our understanding of genetics and has revolutionized the field of molecular biology.
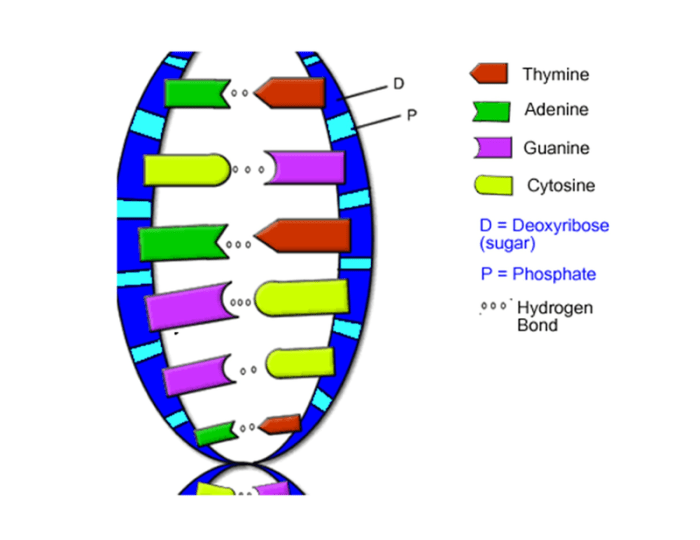
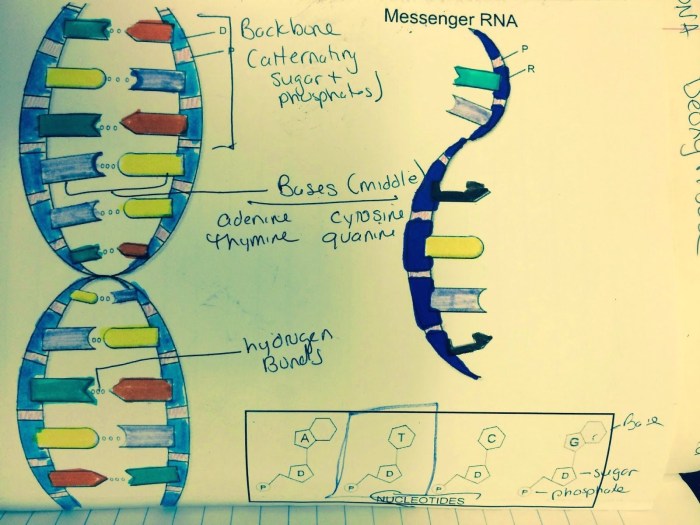
The DNA double helix is a twisted ladder-like structure composed of two strands of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a sugar molecule, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), or cytosine (C).
The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases: A with T and G with C. This base pairing ensures the stability of the DNA molecule and allows for the accurate transmission of genetic information.
Role of Base Pairing in Maintaining the Stability of the DNA Molecule
- Hydrogen bonds between complementary bases (A-T and G-C) form a stable structure.
- The specific pairing rules ensure that the genetic information is accurately copied during DNA replication.
- The double helix structure protects the genetic information from damage.
DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process by which a cell makes an identical copy of its DNA before cell division. This process ensures that each daughter cell receives a complete set of genetic information.
DNA replication is carried out by a complex of enzymes, including DNA polymerase, which synthesizes new DNA strands using the existing DNA as a template. The process involves three main steps: initiation, elongation, and termination.
Importance of DNA Replication for Cell Division and Growth
- Provides each daughter cell with a complete set of genetic information.
- Ensures the continuity of genetic information from one generation to the next.
- Essential for cell growth, repair, and development.
DNA Transcription: Dna Double Helix Worksheet Answer Key
DNA transcription is the process by which the information encoded in DNA is used to synthesize RNA molecules. RNA molecules, such as messenger RNA (mRNA), carry the genetic information from the nucleus to the ribosomes, where proteins are synthesized.
DNA transcription is carried out by an enzyme called RNA polymerase, which binds to specific regions of DNA called promoters. RNA polymerase then synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule using the DNA strand as a template.
Importance of DNA Transcription for Protein Synthesis
- Converts the genetic information in DNA into a form that can be used for protein synthesis.
- Provides the template for protein synthesis.
- Essential for the production of all proteins in the cell.
DNA Translation
DNA translation is the process by which the information encoded in mRNA is used to synthesize proteins. Proteins are essential for all cellular functions, including metabolism, growth, and repair.
DNA translation is carried out by ribosomes, which are large complexes of RNA and protein. Ribosomes bind to mRNA and read the sequence of codons, which are three-nucleotide sequences that specify a particular amino acid. The ribosome then assembles a chain of amino acids based on the sequence of codons.
Importance of DNA Translation for Protein Synthesis, Dna double helix worksheet answer key
- Converts the genetic information in mRNA into a chain of amino acids.
- Produces the proteins necessary for all cellular functions.
- Essential for growth, repair, and development.
DNA Mutations
DNA mutations are changes in the DNA sequence that can occur due to various factors, including errors during DNA replication, exposure to radiation or chemicals, and certain genetic disorders.
DNA mutations can have a range of consequences, from being harmless to causing serious diseases such as cancer. Some mutations can alter the function of a protein, while others may have no effect.
Importance of DNA Repair Mechanisms
- Detect and repair DNA damage to prevent mutations.
- Maintain the integrity of the genetic information.
- Essential for preventing cancer and other diseases caused by DNA mutations.
DNA Technology
DNA technology refers to a wide range of techniques that allow scientists to manipulate and analyze DNA. These techniques have revolutionized the fields of medicine, forensics, and biotechnology.
DNA technology has applications in various fields, including:
- Medicine:Diagnosis and treatment of genetic diseases, development of personalized medicine.
- Forensics:DNA fingerprinting for identification and solving crimes.
- Biotechnology:Genetic engineering, production of pharmaceuticals and biofuels.
Ethical Implications of DNA Technology
The ethical implications of DNA technology include:
- Privacy concerns:Potential misuse of genetic information for discrimination or insurance purposes.
- Eugenics:Concerns about using genetic information to manipulate human traits.
- Gene editing:Ethical considerations regarding the potential consequences of altering the human genome.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of the DNA double helix structure?
The double helix structure of DNA provides remarkable stability, allowing it to store and transmit genetic information with high fidelity.
How does DNA replication occur?
DNA replication is a semi-conservative process where each strand of the original DNA molecule serves as a template for the synthesis of a new complementary strand.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in DNA transcription?
RNA polymerase binds to specific DNA sequences and synthesizes a complementary RNA molecule, carrying the genetic information to the ribosomes for protein synthesis.
How does DNA translation occur?
DNA translation involves ribosomes reading the genetic code in mRNA and assembling the corresponding amino acids into a polypeptide chain.