Embark on a captivating journey through the fascinating world of cells with our comprehensive prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells quiz. This engaging exploration will illuminate the fundamental differences between these two distinct cell types, unraveling their intricate structures, specialized organelles, and unique reproductive mechanisms.
Delve into the realm of prokaryotic cells, uncovering their simple yet efficient organization. Contrast this with the remarkable complexity of eukaryotic cells, boasting a membrane-bound nucleus and an array of specialized organelles. Witness the remarkable diversity of cells, from the microscopic marvels of bacteria to the intricate plant and animal cells that form the building blocks of life.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells: Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Cells Quiz
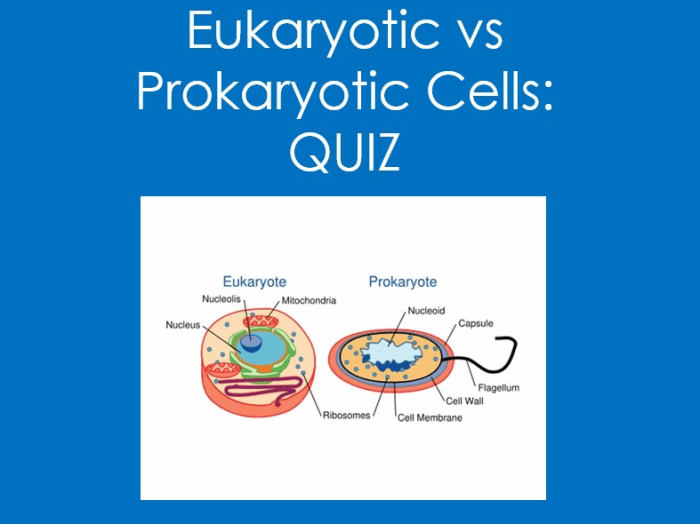
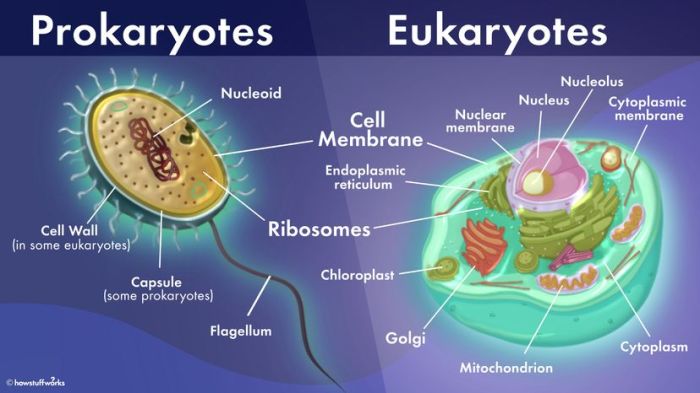
Cells are the fundamental units of life, and they come in two main types: prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells are simpler and smaller than eukaryotic cells, and they lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotic cells, on the other hand, have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, which allow them to perform more complex functions.
Cell Structure
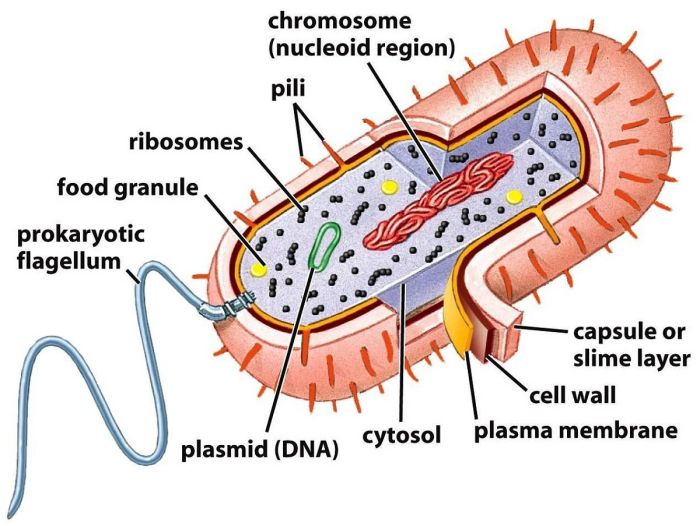
The basic structure of a prokaryotic cell includes a cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA. The cell membrane surrounds the cell and protects its contents. The cytoplasm is a gel-like substance that fills the cell and contains the cell’s organelles. The DNA is the genetic material of the cell and is responsible for controlling the cell’s activities.
Eukaryotic cells have a more complex structure than prokaryotic cells. In addition to the cell membrane, cytoplasm, and DNA, eukaryotic cells also have a nucleus, which is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material. Eukaryotic cells also have other membrane-bound organelles, such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi apparatus, which perform specific functions for the cell.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material. The nucleus is responsible for controlling the cell’s activities and for transmitting genetic information to new cells.
Cell Organelles
| Organelle | Prokaryotic Cells | Eukaryotic Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Ribosomes | Present | Present |
| Mitochondria | Absent | Present |
| Endoplasmic Reticulum | Absent | Present |
| Golgi Apparatus | Absent | Present |
Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis. Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy for the cell. The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins. The Golgi apparatus is an organelle that modifies and packages proteins for secretion.
Cell Reproduction, Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells quiz
Prokaryotic cells reproduce by binary fission, which is a process in which the cell simply splits in two. Eukaryotic cells reproduce by mitosis, which is a more complex process that involves the division of the nucleus and the cytoplasm.
Binary fission is a simple process that occurs quickly. Mitosis is a more complex process that takes longer to complete. However, mitosis is also more accurate than binary fission, which means that it is less likely to produce errors in the daughter cells.
Cell Diversity
There are many different types of prokaryotic cells, including bacteria and archaea. Bacteria are the most common type of prokaryotic cell, and they can be found in a wide variety of habitats, including soil, water, and the human body. Archaea are a less common type of prokaryotic cell, and they are typically found in extreme environments, such as hot springs and deep-sea hydrothermal vents.
There are also many different types of eukaryotic cells, including plant cells, animal cells, and fungal cells. Plant cells are distinguished from animal cells by the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts. Chloroplasts are organelles that contain chlorophyll, which is a green pigment that allows plants to photosynthesize.
Fungal cells are distinguished from plant cells by the presence of a cell wall made of chitin.
Cell diversity is essential for life on Earth. The different types of cells allow organisms to perform a wide variety of functions, and they help to create the complex ecosystems that we see around us.
Clarifying Questions
What is the fundamental difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells?
Prokaryotic cells lack a membrane-bound nucleus and specialized organelles, while eukaryotic cells possess both.
How do prokaryotic cells reproduce?
Prokaryotic cells reproduce through binary fission, a simple division process.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in eukaryotic cells?
The Golgi apparatus modifies, sorts, and packages proteins for secretion or storage.